Your Shopping campaign is not generating sales? You’ve come to the right place! In this article, I’ll walk you through the best tactics to supercharge your Google Shopping ads optimization game.
Let’s get into it!
Table of Contents
Why do you need to optimize your Google Shopping campaign?
Google Shopping campaign is set up in Google Ads dashboard in order to display sponsored content related to a search query.
For example, when a user searches for the keyword “blanket”, you will see the shopping ads appear at the top of the search results page like this:
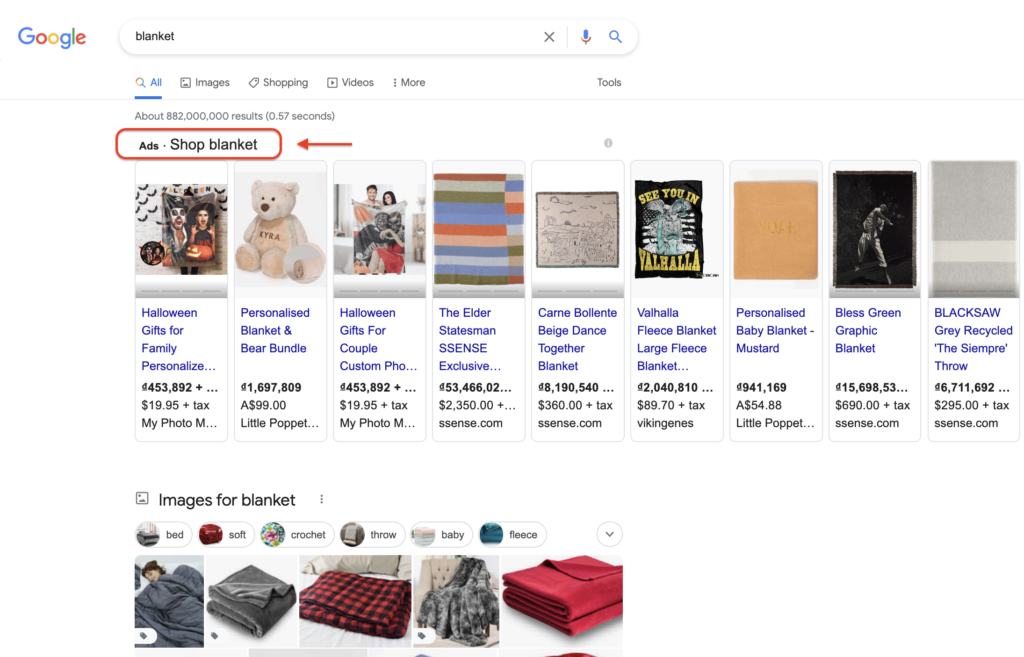
Google Shopping ads for keyword blanket
As you might think, these ads will usually have a relatively high number of purchases and clicks, especially the products that are in the top positions. Therefore, it is not an exaggeration to say Google Shopping ads lie behind the success of many e-merchants these days.
Even though Google does most of the hard tasks for you, don’t just leave your ads to Google by following their recommendations or default settings.
If you want to stand out from the crowd, you have to start the Google Shopping ads optimization process right now.
It is a lot of time and effort but trust me, the results will be well worth your time. Below are some easy but powerful hacks you can apply to bring your shopping ads to the next level.
Winning Google Shopping ads optimization checklist
Use negative keywords
Unlike search ads, shopping ads don’t allow you to define which keywords you want to rank for. They use your data feed to decide which search query should trigger your ads to show.
That is when negative keywords come into play!
Negative keywords allow you to exclude those search terms that don’t match your potential customer’s buying intent.
In other words, using negative keywords is a way of telling people what terms you don’t want your shopping ads to show for.
For example, if you’re selling “white wooden computer desk”, you obviously won’t want your ads to show when people search for the term “white laptop”.
People who are looking to buy a laptop might not care about the desk that you’re advertising for. Meanwhile, Google charges you for every single click.
As a result, you’re wasting money without gaining much or even no profit.
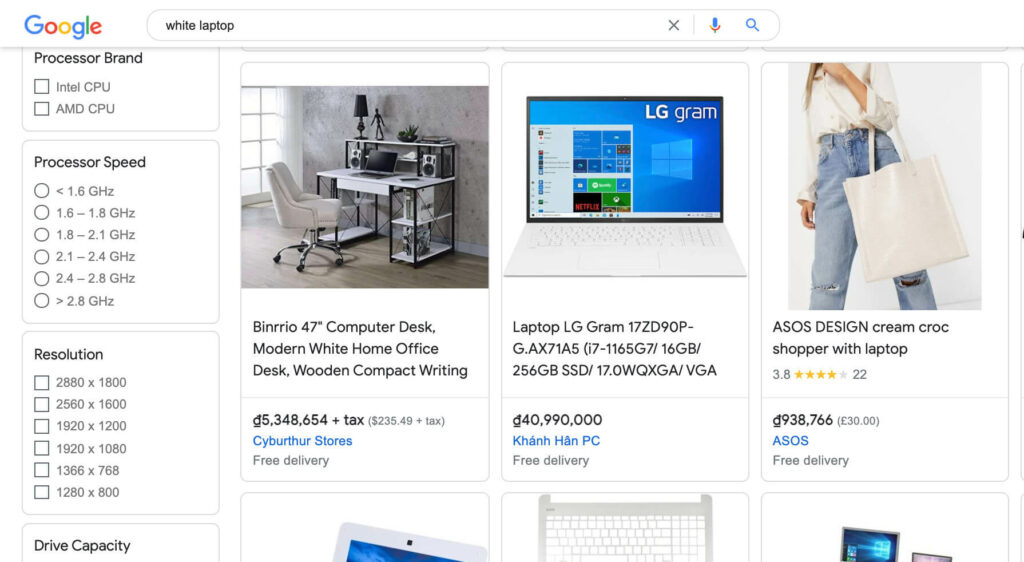
Google Shopping search results for white laptop
In this case, you can add “white laptop” as your negative keyword. Next time, your ads won’t show to the users who search for white laptop and you can thereby save a lot of money.
How many types of negative keywords are there?
There are essentially 3 types of negative keywords: broad match, phrase match and exact match.
- Broad match: the search query won’t trigger your ads if the user searches for the terms you have installed even in different orders.
- Phrase match: the search query won’t show your sponsored content if the user looks up the exact terms you set along with other words or characters.
- Exact match: only use the negative exact match when you want to block ads to people searching for these keywords in particular and do not include any other phrases or characters.
So how do I know which keywords are costly?
From your Google Ads report, go to your campaign. Click on “Search terms”. From here you can see all the keywords that your shopping ads are getting clicks from.
Simply sort out the keywords that you find not relevant to the products you are selling, getting many visits but no sales.
Navigate the Negative keywords section, simply type or paste your chosen keywords in the grid. Click Process.
Pro tips:
- If you want to include broad match keywords, make sure to add their synonyms, singular & plural versions and other variations.
- With phrase match keywords, put them in “quotation quotes”.
- Put exact match keywords in [brackets].
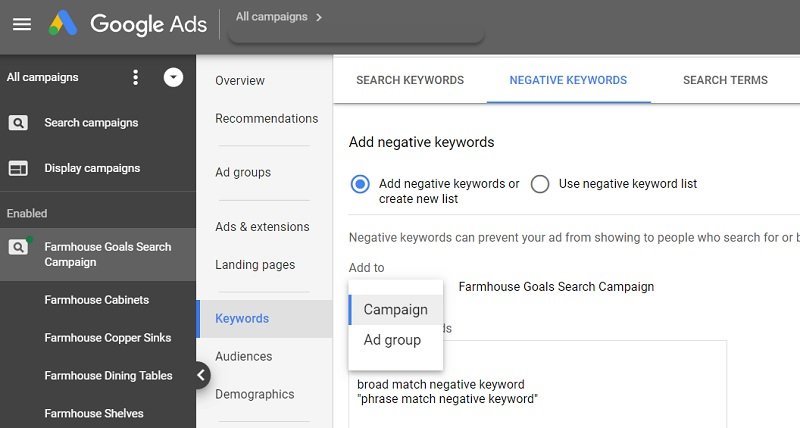
Add negative keywords in Google Ads
Moving on to the next tips in our Google Shopping ads optimization checklist, which is improving your product feed.
Optimize your product feed
An optimized product feed is of utmost importance to Google Shopping ads optimization process. Our recommendation is to pay close attention to the most heavy-weighted fields like product title, image, and description. Let’s see what we can do!
Product title
Google actually reads product titles to understand what you’re selling and decide whether your item is relevant to a certain search query.
Therefore, what you put into your product titles has a significant influence on the effectiveness of your Shopping Ads campaign. Here are some must-try tips to optimize your Google Shopping product titles.
Write long and clear product titles.
Vague and short titles like “electric device” could cause a lot of confusion for buyers since it has failed to specify which device you’re selling or simply which brand it belongs to. As a result, the chances of users clicking on your shopping ads would be very low.
Hence, it is crucial to make sure whoever reads your product titles knows exactly what your product is about.
Add necessary keywords.
Google utilizes the attributes in your product titles as keywords. On a regular basis, the Google bot scans those keywords to determine which inquiries your shopping ads are most relevant for.
Hence, one of the best strategies is to carefully analyze your customers’ buying behavior to figure out which keywords they usually use to look for your products. The Google ads search terms report could be your best buddy in this case.
Place important keywords upfront.
The search engine algorithm values information that is put in the forefront position in the title. On that grounds, you’d better show off the most outstanding features or unique selling points of your items in the first 70 characters. In the long run, this strategy could really benefit our google shopping ads optimization process.
Create titles for each product variant.
For example, you’re selling a short-sleeved white t-shirt for men and it has 2 variants: size S and size M. There should be 2 titles: “Short-sleeved white t-shirt for men size S” and “Short-sleeved white t-shirt for men size M”.
Follow the recommended product title structures.
To produce the best product title for each given product category, there is a universal product title structure and formula that you should use. Here are some examples to help you understand how to organize your Google Shopping product names for whatever you are selling.

Google Shopping product titles’ recommended structures and examples
A/B testing
Product title optimization is something you have to do on a regular basis in your Google Shopping ads optimization journey. My advice is to constantly evaluate your campaign’s performance report, figure out the best and worst-performing products. You’ll soon have your own formulas.
Product description
While a good title makes users want to know more about your product, a nicely written Google product description would provide more information about your item and give shoppers a reason to buy your product.
Pretty similar to product titles, a good description should:
Include the most important information in the first 145-180 characters.
Since the Google Shopping SERPs only present these characters to your visitors, you should establish a hierarchy in which you will arrange your product information.
Here is an example of the hierarchy:
- Brand
- USP of the product
- Who the product is for
- Other relevant attributes
Include the most relevant attributes and keywords.
You should never leave out the size, shape, pattern, texture, design, or technical specs of the products in the description. This is your golden chance of letting the shoppers know more about your products and decide whether it is a good fit or not.
Keep it as concise as possible.
Although Google Shopping allows you to add up to 5000 characters for this field, you should only use between 500 and 1000 characters.
Writing the description too long may distract the buyer since they don’t know where to look. In the long run, this could negatively affect your Google Shopping ads optimization goals.
Moreover, there are certain things you should not incorporate into your description field:
- Promotions
- Block capitalization
- Cross-selling
- Company description
- Links to other websites
Product image
Online shoppers make an instant assessment based on the design/ image of your products.
The more accurate and appealing your product images look compared to other products of the same kind, the more likely you’ll get their clicks.
That said, taking advantage of the product image section is another key step in google shopping ads optimization.
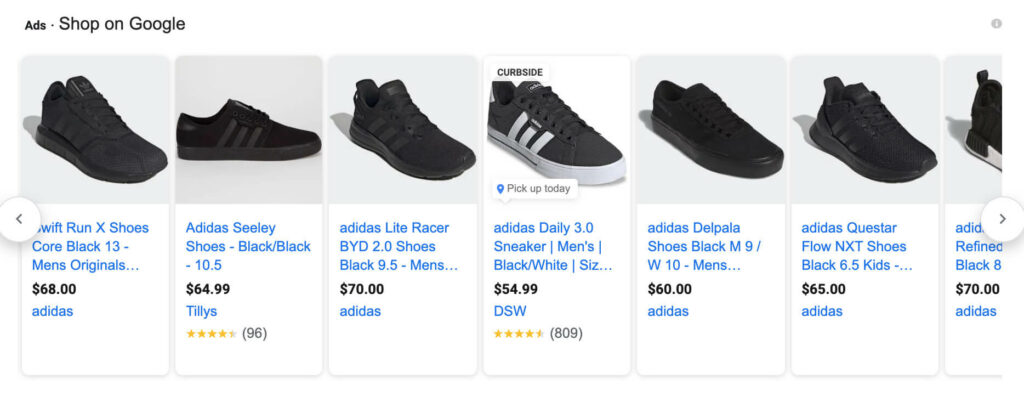
Black Adidas shoes product images
It would be best to add at least 3 pictures to show different angles of your items.
In other words, you must have a minimum of 2 additional images to clearly show your products and impress buyers.
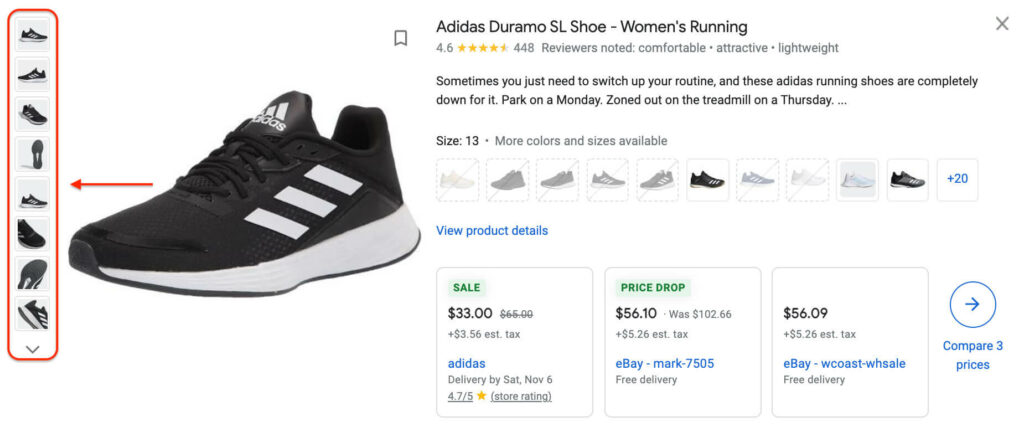
Additional images of Adidas Duramo SL Shoe
Pro tips:
- To ensure your product is the most prominent object in the picture, shoot it on a white background.
- Remember to attach product images to their matching variants. For instance, you’re advertising for a black pair of shoes and the picture is showing the white version of the shoes, shoppers may not want to click on your ads let alone buy something from your store.
Find best and worst-performing products
In any Google Shopping campaign, there will always be some products that are performing better than others and some are not generating as many sales. Store owners can take advantage of this insight to maximize their Google Shopping ads optimization results.
Since you have to pay for every single click, you don’t just want to show your products. Instead, you want the actual conversions from the ads.
On that account top-performing products are the ones with the most conversions and the lowest CPC. Likewise, the worst-performing products have a lot of visits but no sales.
Where could I find those products’ information?
From your Google Ads dashboard, select Report > Predefined reports (Dimensions) > Auction insights.
Then select how you want to see your products by shopping account, campaign, or ad group. Opt for the Shopping – Campaign option.
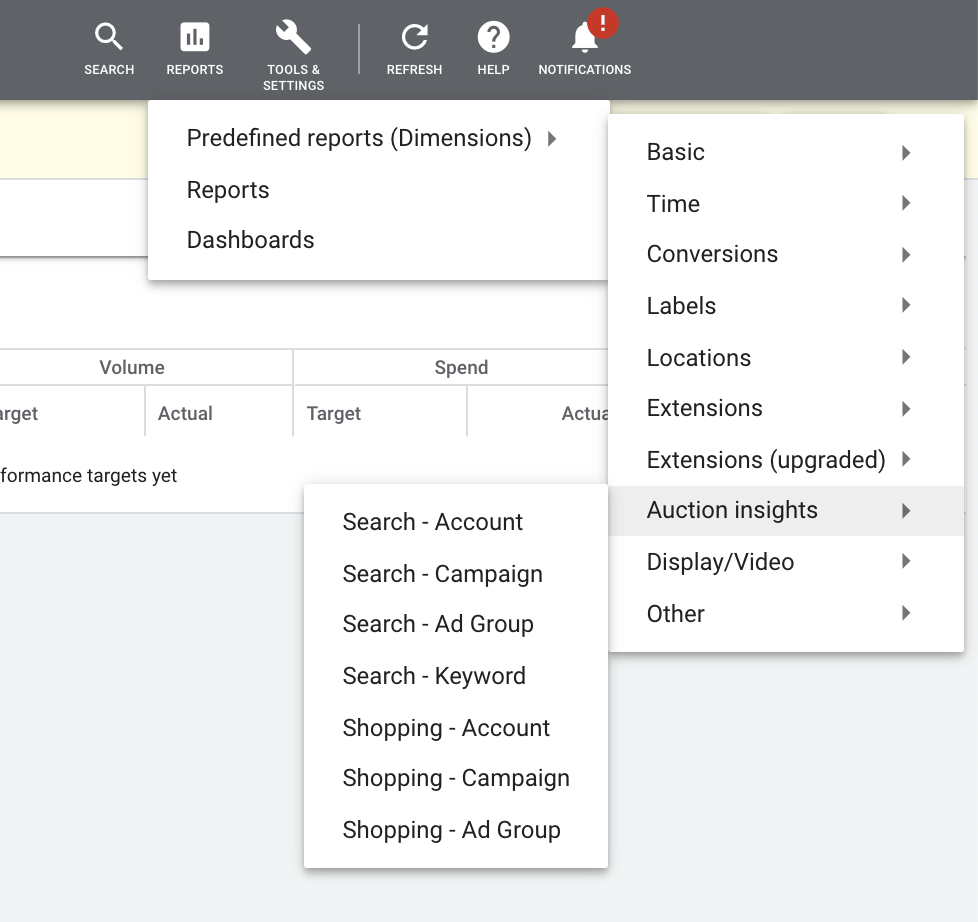
Google Ads predefined reports
From here Google ads allows you to select the metrics and dimensions to customize the report.
It is a good idea to choose the dimensions that match the structure of your campaign. This way you can identify the winners and losers for each product group.
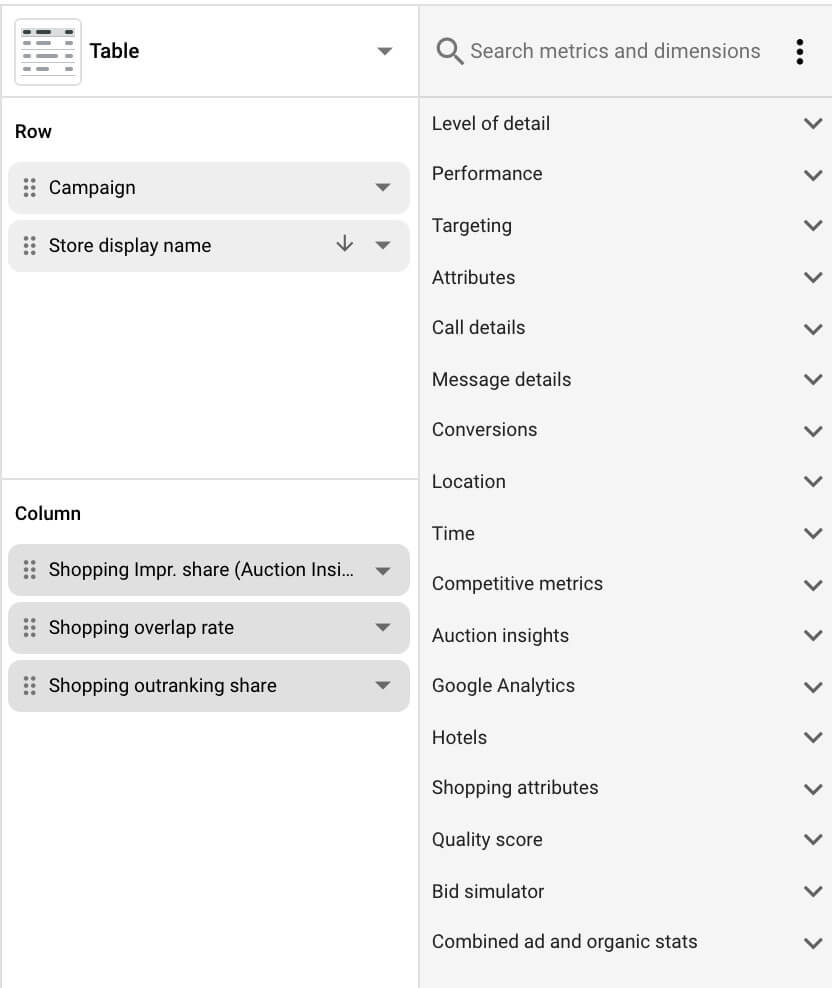
Select metrics and dimensions for Google Ads report
One important thing to remember is that you can filter products based on the market to maximize the results.
For example, it’s common for luxury brands to have many clicks but only 1-2 conversions. On the contrary, those products would be marked as bad performers if they are in the clothing category.
In addition, pay attention to the cost per conversion columns. If the cost per conversion for an item is higher than your profit margin, your money is clearly not well-spent.
Now that you have identified the top and worst-performing products, go back to the Product Groups tab and adjust your bids. Bid more on the former and bid less on the latter.
Optimize your Google Shopping campaign structure
An appropriate structure enables merchants to bid on the most highly converting products and keywords. Therefore, choosing a suitable campaign structure is one of the determining steps of your Google Shopping ads optimization process.
“What is the best Google Shopping campaign structure?” is the question that a lot of e-merchants want to have the exact answer.
Unfortunately, there is no right or wrong structure for google shopping ads optimization. But there are some positives and negatives to each structure that you can use.
In this article, I’ll evaluate the 4 most common campaign structures:
Structure 1 – 1 campaign, 1 ad group, 1 product group, use the same bid for all products
With this structure, you have only 1 campaign, 1 ad group, 1 product group and in that product group, every product has the exact same bid.
This could mean that when you first start creating your campaign, you follow the Google recommendations and don’t make any changes. In this case, every item and keyword receive the same investment and are equally important to your business.
With this type of campaign structure, you cannot control your bid on the product level. All you can do is raise the max CPC for all products.
I will not recommend this structure for any store owners unless you are just starting out and you have no idea which products should receive more financing than the others.
These campaigns can still get results. However, if you want to bring your Google Shopping ads optimization game to the next level, explore the other options below!
Structure 2 – 1 campaign, 1 ad group with multiple product groups
This campaign structure allows you to subdivide your products into category, brand, item ID, condition, product type, channel, channel exclusivity or even custom label.
Google also enables you to split your products into multiple levels. For example, you can first split your products by brand and then split them one more time by item ID.
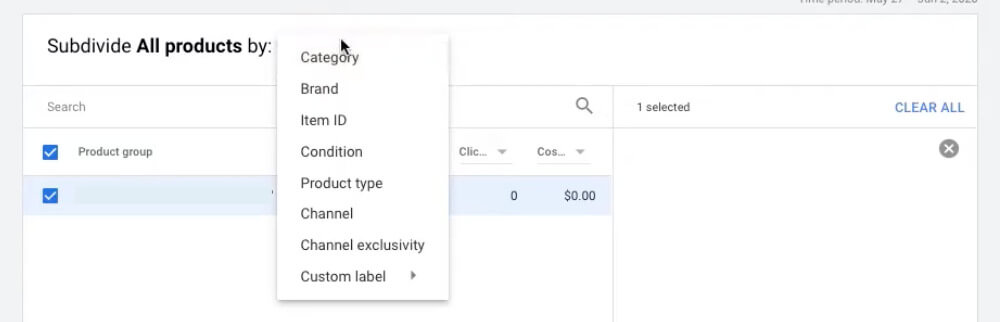
Subdivide products by attributes
Okay now you can bid on those attributes to ensure the best results from your google shopping ads optimization progress or if you choose the items ID option, you can bid differently on every single product.
Keep reading to the next section to know how you can effectively manage those bids!
This structure is probably the most widely used one because it is simple but still gives you a lot of control over your investment in each product in groups/ individuals. Here are some pros and cons to this:
- Pros:
- It’s very easy to set up and manage.
- Since there’s only 1 campaign, you only have to manage 1 source of money.
- You can maintain all of your bids and negative keywords in one place.
- Cons:
- Since you only have 1 campaign, all of your budgets go into that campaign. If certain products are performing extra well, the advertisements for those campaigns are still restricted by the budget for the whole campaign.
- You can’t set negative keywords on the product level.
Structure 3 – Multi-campaigns with the same product group
Google Shopping allows us to create a campaign for certain attributes like we mentioned above: category, brand, item ID and etc.
So just like the name, with this structure, you have to manage more than one campaign at a time. This means you have the right to set negative keywords and prioritization settings to funnel traffic to different campaigns based on search queries.
For example, if you want to split your campaigns based on your potential customers’ buying journey you have carefully studied, you can create different campaigns for Brands, SKUs, or other generic search queries. Then you are able to bid aggressively on branding campaigns but less money goes into the generic search queries one supposing your business goal is branding.
Then set the campaign priority of the branding ads to high and the SKUs to medium and generic search to low.
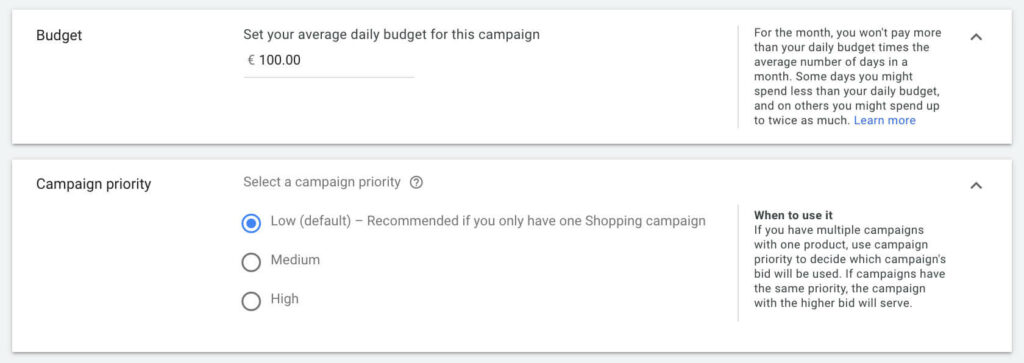
Set campaign priority in Google Ads
What are the benefits of this structure?
- You will have more control over your budget for each campaign. For this reason, you can allocate your budget more effectively, focusing on what is more profitable to your business.
- You’ll be able to manage bids not just on the product level but also based on the search queries that people are using to see your shopping ads.
On that ground, adopting this structure is also a good measurement for our google shopping ads optimization.
However, it has certain limitations:
- It’s very complicated to manage on a daily basis. In order to get the hang of this multi-campaign structure, you have to spend a lot of time and effort learning how it works. Hence, don’t choose this structure if you’re just starting out or you don’t have expert knowledge about Google Shopping.
- Since there is more and one campaign, it’s harder to manage and keep track of the reports coming from different sources.
In short, the biggest advantage of using this structure is that you are able to establish distinctive maximum CPCs depending on how profitable a search query is to you.
However, don’t touch on this if you are newbies and or you are not generating enough conversions for Google to learn the data and decide who would most likely enjoy your ads.
Structure 4 – Multiple campaigns with only the most high-converting products
These are the winning products of your ongoing campaigns and you clearly don’t want to limit the budget for those products by putting them in the same campaign with a limited budget like the others.
In this case, go ahead and exclude those products from the original campaigns, and then create a new campaign.
From your campaign Settings > navigate Inventory Filter > select Product Attribute as Item ID > Tick on your top performers > Click Save.
Choose the right bidding strategy
Now that you have done all the steps above, it’s time to get your max CPCs right for further Google Shopping ads optimization.
Generally, you have 2 bidding options:
- Automated bid strategies: This essentially means that you let Google do the job. The search engine will decide how much you have to pay for one click.
- Manual CPC: You have to do all the work from evaluating reports, setting bids on the product level, managing and adjusting bids on a daily basis.
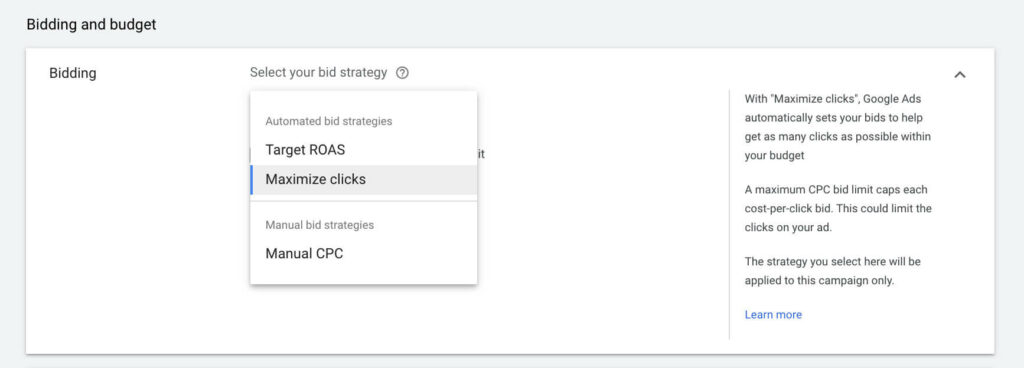
Bidding strategies for Google Shopping
When to raise the max CPCs for your campaign?
The most appropriate time is when you are getting many conversions and profits, you expand your ads spend in order to gain more traffic and sales to your store.
Keep in mind that: You wish to get more orders at the lowest cost, but Google doesn’t care about your profit margin. All they care about is making you spend more on its platform.
Therefore, if you give Google all the rights to control your bidding, you might not be able to fully optimize your shopping campaign.
In this section, I’ll give you more details about each bidding strategy, helping you to choose the right one for your google shopping ads optimization.
#1. Manual CPC
This bidding strategy means that you have to go through your report and note down which item or attribute you want to adjust its CPCs and manually modify the bids based on what you see.
For instance: In one campaign you’re selling 50 different kinds of cups. Out of the collections, 2 designs are selling like hotcakes but you still want them to gain more clicks. Thus, you decide to raise the CPC of each cup by $0.2. Then 1-2 days later you might get the desired clicks.
This bidding method will be pretty time-consuming but it gives you 100% control over your bid. I always recommend manual CPC for e-merchants especially if you run a small to medium-sized business.
#2. Maximize clicks
With this strategy, you’re asking Google to modify your bid just to get more clicks. Not more sales.
Since Google knows exactly which products or clicks are the cheapest, the search engine will base on that to distribute your budget and thereby get as many clicks as possible.
But bear in mind that you can’t make money out of clicks. Your goal is to actually sell the products, make profits by Google Shopping ads optimization approach.
For that reason, I recommend you stay away from this strategy.
#3. Target ROAS
Target ROAS is equal to Target Return On Ad Spend. By using this strategy, you’ll be able to set your expected conversion value for every buck you spend.
Let’s look at an example: You expect to receive $6 back for every $1 you spend, just set your Target ROAS as 600%.
Please not: this is just your EXPECTATION. Google doesn’t guarantee you will get your desired ROAS. You can have more or less.
Then how do I ensure that the revenue will be as close to your target or better?
The only solution is to provide Google with enough information.
To be more specific, you need to bid using the manual method first and get at least 50-100 conversions before opting for this strategy. Because those first conversions are crucial in giving google decent data about your visitors and buyers in order for it to better decide who to show the ads for.
Now let’s move on to the last tactics in our Google Shopping ads optimization checklist!
Target more specific location
A lot of retailers overlook the importance of location targeting, they can simply include the country name as their target market.
This is not optimized at all. If you are selling items like thermal bags or duvets and you’re targeting the entire country where half of it is in the hot weather, you’re putting half of your money in trash.
Instead, research more on the locations where you can get the most conversions from and implement a geographic bid modification strategy. This is where the Dimensions tab comes in handy.
Final thoughts
And there you have all the top tips that you can apply to get the best results while implementing Google Shopping Ads optimization.
Don’t forget to try these tips out and let us know your amazing outcomes!
 socialhead
socialhead